Thermoforming
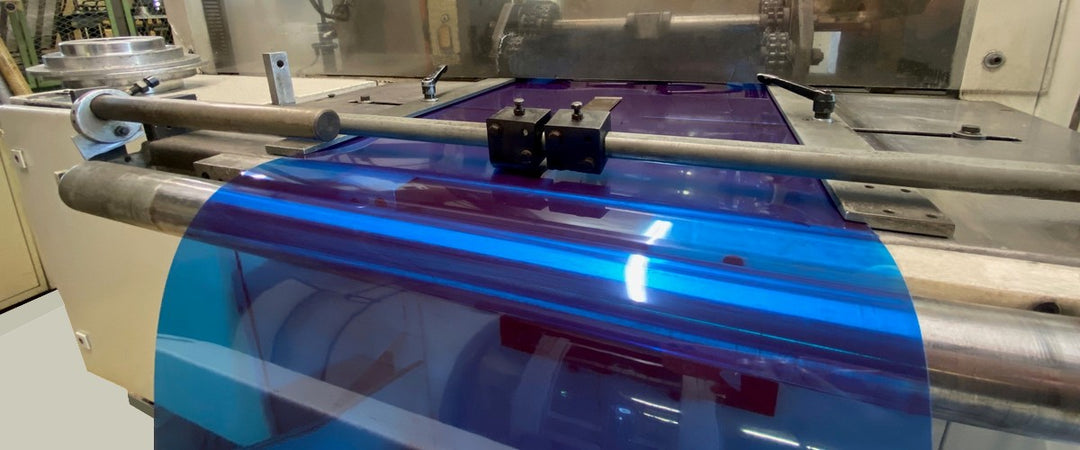
Thermoforming is a manufacturing process that shapes plastic sheets using heat and pressure. It is widely used in industry to produce packaging, trays, casings and other plastic products. The principle of thermoforming consists of heating a sheet of plastic until it becomes flexible, then placing it on a mold where it will take the desired shape. Once cooled, the plastic retains this solid shape.
The main advantages
Thermoforming has several advantages over other plastic processing techniques.
First of all, it is relatively economical , as it requires less investment in equipment and tools than other methods like injection or blow molding.
In addition, thermoforming allows great design flexibility, as it is possible to produce complex shapes and precise details. This adaptability makes it possible to meet specific customer needs and create tailor-made products.
Another major advantage of thermoforming is its speed . Production cycles are generally short , which makes it possible to quickly obtain prototypes or production runs in large quantities. In addition, thermoforming offers a wide variety of available materials , such as PVC, PET, polystyrene, acrylic, which allows you to choose the material best suited to the requirements of the final product.
One of the most virtuous processes
Thermoforming is a plastic processing technique which is considered one of the most environmentally friendly : it generates less waste and loss of material than other processing techniques. Plastic waste can be recycled and reused, contributing to sustainability and reducing the carbon footprint. It is therefore an efficient, economical and versatile manufacturing process, offering many advantages over other plastic processing techniques. Its adaptability, speed of production and reduced environmental impact make it an attractive solution for many industrial applications.
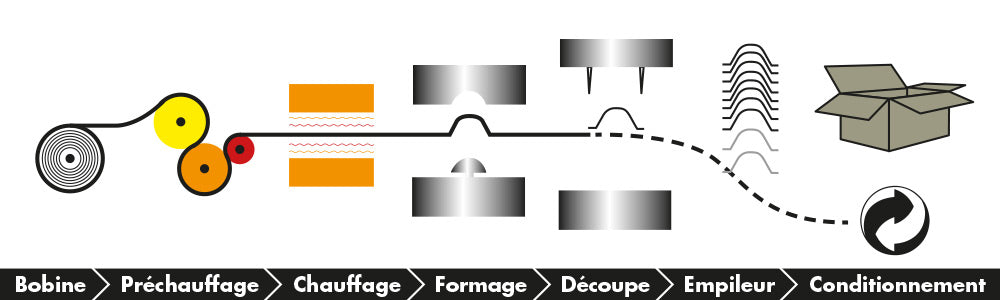
The stages of thermoforming
1. Raw materials
PETIT is able to transform a large number of plastic materials such as PP, APET, PVC, PS as well as their derivatives (expanded, complexed).
2. Preheating
Consists of passing the film over heated rollers to prepare the material and allow higher temperatures to be reached.
3. Heating
Each material is heated via radiants to different temperatures depending on its physicochemical properties.
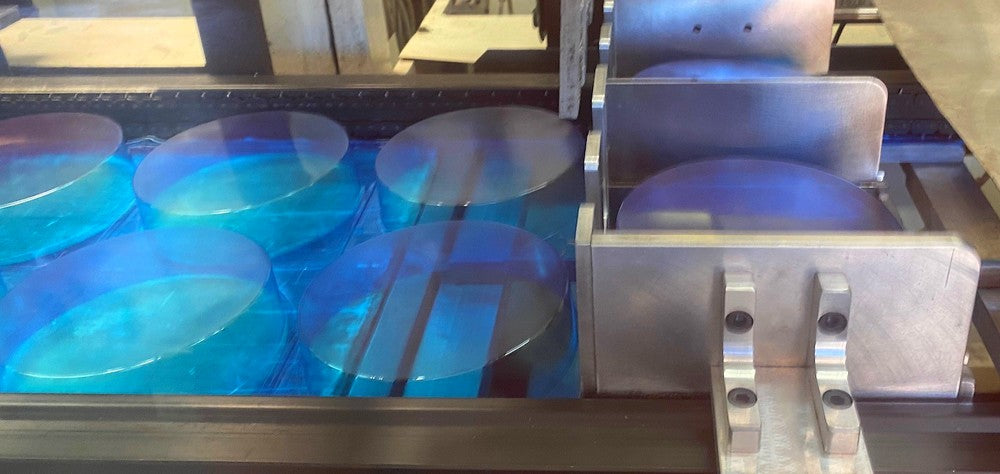
4. Forming
Forming is the step where the part takes shape. Depending on its geometry (height, development, etc.), a piston may be necessary for the correct forming of the parts.
5. Cutting
Once the parts are formed, they are cut individually and the excess material is eliminated. These surpluses are collected: they are then recovered by specialists in the plastic recycling sectors.
6. Automatic stacking
The trays are stacked and come out of the stacker to be packaged.
7. Packaging
The parts produced are placed in food grade plastic bags, and placed inside the boxes then installed on a film-covered pallet.